
アルツハイマー病治療薬候補のアデュカヌマブの治験中間結果は「不十分」という結論 --- 大きな副作用、はっきりしない効果
アルツハイマー病でなくても高齢になるだけで認知機能が年間0.13 (MMSEベース) 下がるのに、アミロイドβ低減しても0.03しか改善しないなら治療の効果なくね? それってそもそもアミロイドβがアルツハイマー病の原因じゃなくね? ってまっとうな意見
ICERの中間報告、審査中のアデュカヌマブは「有益性の根拠が不十分」
https://bio.nikkeibp.co.jp/atcl/news/p1/21/05/19/08173/
非営利の医療技術評価(HTA)機関である米臨床経済評価研究所(ICER:Institute for Clinical and Economic Review)は2021年5月5日、米食品医薬品局(FDA)が現在承認審査中のアルツハイマー病(AD)の疾患修飾薬アデュカヌマブについて、「Aducanumab for Alzheimer’s Disease:Effectiveness and Value」と題するエビデンスレポートの草案(Draft Evidence Report)を公表した。副作用のリスクと有効性の不確かさの観点から、健康上の利益をもたらすことを示すエビデンスの強さを、暫定的に「不十分」と指摘した。
ICER Releases Draft Evidence Report on Aducanumab for Alzheimer’s Disease
https://icer.org/news-insights/press-releases/icer-releases-draft-evidence-report-on-aducanumab-for-alzheimers-disease/
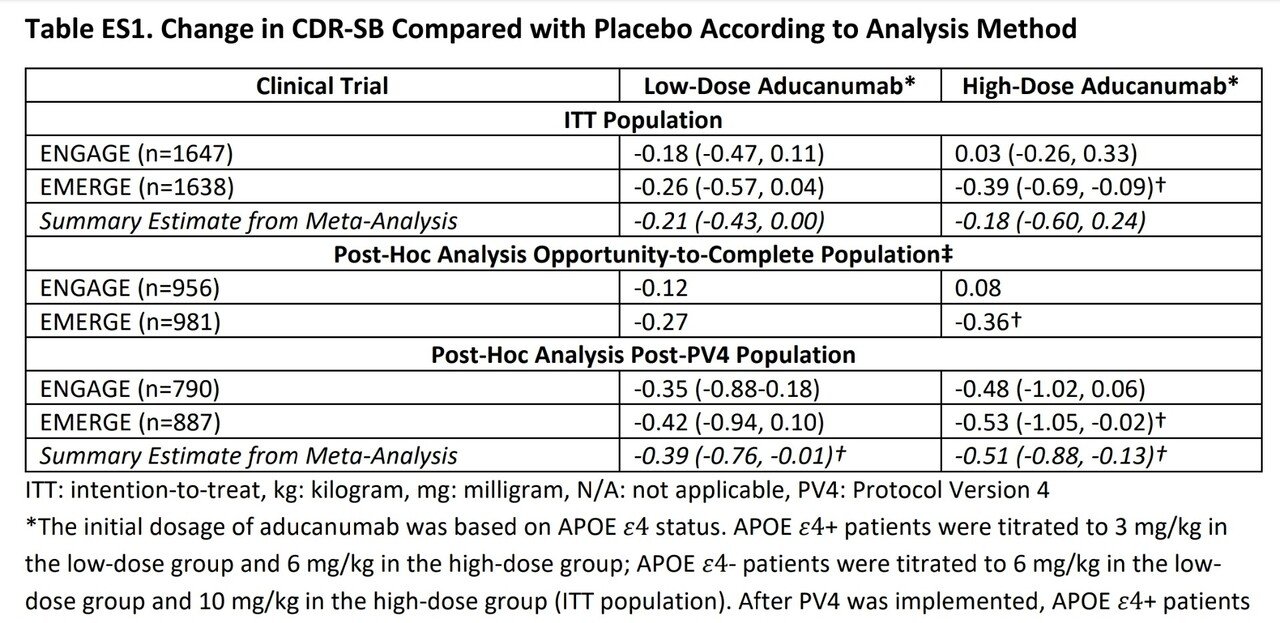
2種の治験(EMERGE と ENGARE)、2種類の投与量のかけ合わせて4種類の治験結果が出ている。そのうちEMERGEの高用量群だけが統計的に有意な結果となった。
治験がうまく行かなかった(が実際には有益だと主張したい)理由を説明するための事後解析では、治験ではAPOE ε4 というADのマーカーによって用量を切り替えていたそう。つまり治験結果のばらつきはこの投与量の変更というノイズが原因だった可能性が出てきたが、用量を固定した解析ではその可能性は排除された。メタアナリシスによる解析では低用量群ではCDR-SB値が平均0.39の改善、高用量群では平均0.51の改善となった。
また副作用に関してはアミロイド関連画像異常が35%に発生していた。
Q&A: Questions remain about the efficacy, safety of aducanumab for Alzheimer’s disease
https://www.healio.com/news/neurology/20210519/qa-questions-remain-about-the-efficacy-safety-of-aducanumab-for-ad
Healio Neurology: Can you provide an overview of your main points?
Alexander: Two nearly identical pivotal trials of aducanumab were conducted, one of which failed and the other which suggested a possible very modest effect in one of two treatment arms. While there is historical precedent for the FDA approving a product based on a substantial evidence from a single adequate and well-controlled clinical trial, the evidence generated for aducanumab doesn’t meet this threshold. Aducanumab’s sponsor, Biogen, has undertaken several post-hoc analyses to explain why the trial results weren’t more compelling; these post-hoc analyses may be useful for hypothesis generation, but also introduce unacceptable threats to statistical validity in this type of setting. In other words, it is always easier to explain why your team lost on the day after the big game.
In addition, there are potentially serious concerns regarding aducanumab’s safety that must be considered as well, including the relatively common prevalence of amyloid-related imaging abnormalities, or ARIA, that, in some cases, can be quite severe and may also be hard to disentangle from AD itself.
Evaluation of Aducanumab for Alzheimer Disease
Scientific Evidence and Regulatory Review Involving Efficacy, Safety, and Futility (2021)
https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jama/article-abstract/2778191
Effect of reductions in amyloid levels on cognitive change in randomized trials: instrumental variable meta-analysis
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33632704/
Results: Pooled results from the 14 randomized controlled trials were more precise than estimates from any single trial. The pooled estimate for the effect of reducing amyloid levels by 0.1 standardized uptake value ratio units was an improvement in the mini-mental state examination score of 0.03 (95% confidence interval -0.06 to 0.1) points. This study provides a web application that allows for the re-estimation of the results when new data become available and illustrates the magnitude of the new evidence that would be necessary to achieve a pooled estimate supporting the benefit of reducing amyloid levels.
Conclusions: Pooled evidence from available trials reporting both reduction in amyloid levels and change in cognition suggests that amyloid reduction strategies do not substantially improve cognition.
14のランダム化コントロール試験を用いたメタアナリシスによると、アミロイドβを0.1低減しても、認知機能は有意な改善を見せなかった。つまりアミロイドβはアルツハイマー病の原因ではない可能性が高まった。
Anti-amyloid trials raise scientific and ethical questions
https://www.bmj.com/content/372/bmj.n805.full
1 After a significant reduction in brain β-amyloid, there was a non-significant change of 0.03 (95% confidence interval −0.06 to 0.1) points in the mini mental state examination. This score (maximum 30 points) declines by about 0.13 points a year in older people in the community,
2 dropping more rapidly in those with cognitive impairment or dementia. Scientists should seriously question the validity of the basic amyloid hypothesis, as was pointed out more than 10 years ago in relation to earlier trials.
3 These findings should direct our attention to the prevention of Alzheimer’s disease by slowing down the disease process, for which there are many possible approaches.
認知症の有無に関わらず高齢になるとミニメンタルステート検査(MMSE、認知機能検査)は年平均0.13減少するのに対して、アミロイドβ治療薬は0.03の改善しかもたらさないことは、この手法には実質的な意味がないということになる。
この記事が気に入ったらサポートをしてみませんか?
