Specular reflections and diffuse light鏡面反射と拡散光
水やガラスなどの透明な素材を除くと私たちは主に物体の表面で跳ね返った光を見ているこのになります。この現象は大きくスペキュラー(鏡面反射)とディフューズ(拡散光)の2つに分けることができ、また物質は導体(Conductor)と誘電体 (Dielectric)に分けて考えることができます。
Except for transparent materials such as water and glass, we mainly see light bouncing off the surface of objects. This phenomenon can be divided into two main categories: specular and diffuse, and materials can be divided into two categories: conductors and dielectrics.
This is a copy from kyndinfo.notion.site and is part of the articles on light and 3D rendering. Here's the original page.
このページはkyndinfo.notion.site からの転載で、光と3Dレンダリングについて書いた記事の一部です。元のページはこちら。
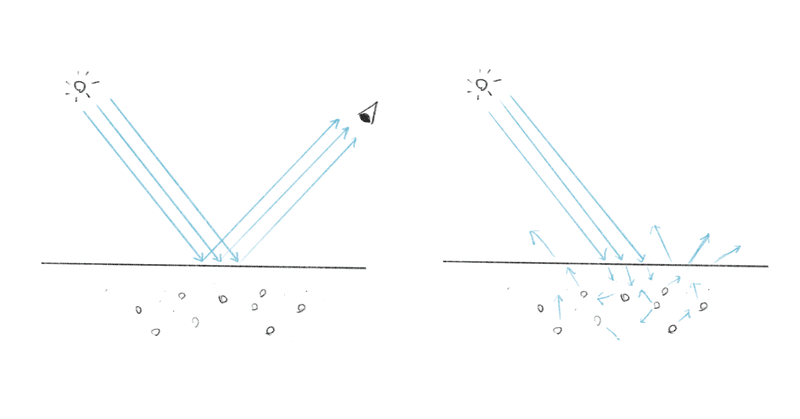
Diffuse and specular reflections
ディフューズとスペキュラー
Reflection of light on an object can be divided into specular and diffuse. Part of the light is reflected directly on the surface of the object and reaches the eyes. The rest of the light goes into the material and diffuses in various directions. When this happens, the material absorbs some frequencies affecting the color of the light coming out. The reason black materials accumulate more heat than white under the sun is that black materials absorb most frequency bands.
物体に当たる光の反射はスペキュラー(鏡面反射)とディフューズ(拡散光)に分けることができます。光の一部は物体の表面でそのまま反射されて目に届きます。残りの光は一旦物質の中に入って乱反射し、様々な方向に散らばります。このときに一部の周波数の光が吸収されることで出てくる光の色が変わります。吸収された分の光は主に熱に変わります。日に当てた時に白いものよりも黒の方が熱を溜め込みやすいのは黒い物質はほとんどの周波数帯を吸収してしまうからです。

Conductor or dielectric
導体と誘電体
The relationship between specular and diffuse depends on if the material is conductor or dielectric (roughly metallic and non-metallic).
スペキュラーとディフューズの関係は導体(Conductor)と誘電体 (Dielectric)(大雑把に金属と非金属)で異なります。
Conductor
導体
Conductor has no diffuse component, only specular. Also, the specular in the conductor will be colored. Metals mirror much of the light that hits them in a specular way, but once inside, light never comes out (as visible light). Imagine a shiny gold reflecting its surroundings with a yellow-ish tint.
導体にはディフューズ成分がなくスペキュラーだけになります。金属は当たった光の多くを鏡面反射しますが、一旦中に入った光は(可視光線としては)出てくることがありません。また導体のスペキュラーには色が着きます。ピカピカの金の塊に周りの様子が黄色く反射しているところを思い浮かべてください。

Because of the classic CG technique described on the next page, specular is sometimes thought to represent bright highlights but it technically refers to the directly reflected component of light. So in the image above, all reflections on the sphere are specular. The reflection will look blurry on an unpolished surface as the light will be reflected by fine irregularities, but this is also specular reflection and is different from diffuse light that we will discuss next.
次のページで説明する古典的なCG技法のせいでスペキュラーは明るいハイライトを表現するものと思われていることがありますが、より正確には物体に当たった光が直接反射した成分を指すので、上の画像では球体に映った反射全てがスペキュラーです。表面が滑らかでなければ光は細かな凹凸に反射してぼやけて見えることになりますが、これも鏡面反射=スペキュラーで、次に見るディフーズによる拡散光とは別物です。

Dielectric
誘電体
Dielectrics, i.e., most materials other than metals such as plastic and paper, tend to have more diffuse than specular. The color of an object is mainly determined by this diffuse component. Dielectric specular does not have color. I.e., the spectral distribution of the reflected light remains intact. Imagine a red plastic object with a bright highlights. The red color is the diffused light, and the highlight is the specular, which will usually appear white reflecting the color of the light source.
誘電体、つまりプラスチックや紙など金属以外のほとんどの物質ではディフューズ成分の方が多くなります。物体の色は主にこのディフューズ成分で決まります。誘電体のスペキュラーには色がつきません。つまり反射された光のスペクトル分布がそのまま残ることになります。赤いプラスチックの上に明るいハイライトが見える様子を想像してください。赤い色がディフューズ成分、ハイライトはスペキュラーなので光源の色を反映して大抵は白く見えます。

Like metal, plastic also reflects light from the entire surrounding area as specular. However, in the case of plastic, the amount of reflection is much less than that of metal, so the reflection of bright light sources stands out more.
実はプラスチックも上の金属のように周囲全体からの光をスペキュラーとして反射しています。プラスチックの場合は金属に比べてずっと反射の量が少ないので明るい光源の反射だけがより目立って見えるだけです。
The light goes through deeper and more complex pathways in case of translucent objects like human skin. This effect is reproduced by techniques such as Sub Surface Scattering.
人間の肌のように半透明な物体は中に入った光がより深く複雑な経路を通ることになります。この効果はSub Surface Scatteringといった技術によって再現されます。
Next:
Classic 3D Rendering 古典的 3D レンダリング
@kynd Twitter Instagram Vimeo Threads
この記事が気に入ったらサポートをしてみませんか?
