
AtlasⅤ in 3 minutes
AtlasV is a launch vehicle developed by United Launch Alliance (a joint venture between Lockheed Martin and Boeing: ULA).
It was launched from the U.S. spaceports Cape Canaveral Air Force Base and Vandenberg Air Force Base, and has been successful in all but one launch since its initial launch in August 2002.
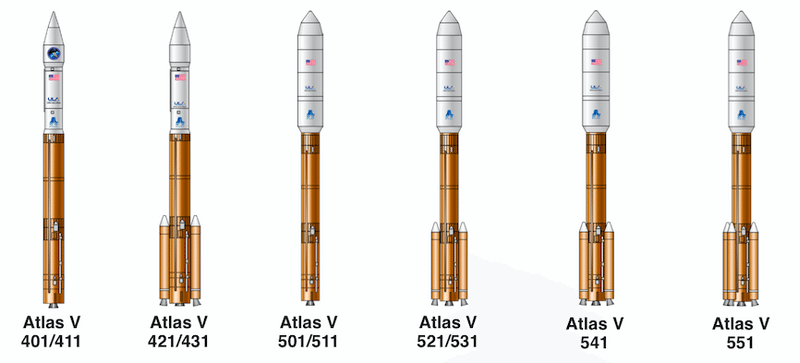
AtlasⅤ has the 400 and 500 series. The 100th digit is the diameter of the fairing, the tip on which the load is placed (4m or 5.4m), the 10th digit is the number of first-stage solid fuel engines, 1 Indicates the number of engines in the second stage (1 or 2).
The total length is 60.6m (75.5m for the 500 series), the first stage with an engine using kerosene and liquid oxygen as a propellant and a maximum of five solid fuel engines, and the second with an engine using liquid hydrogen and liquid oxygen as a propellant. It consists of fairings with different shapes depending on the tier and series.
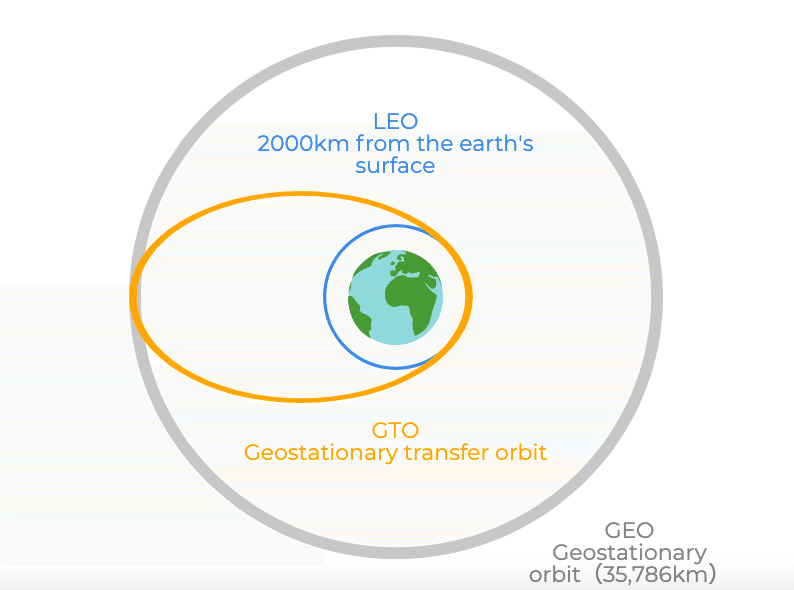
It can transport 18850kg to low earth orbit (LEO) and 15179 kg to geostationary transfer orbit (GTO) before transferring the satellite in geostationary orbit. The price is about 10.9 billion to 17.9 billion yen.
Reflight / refund service
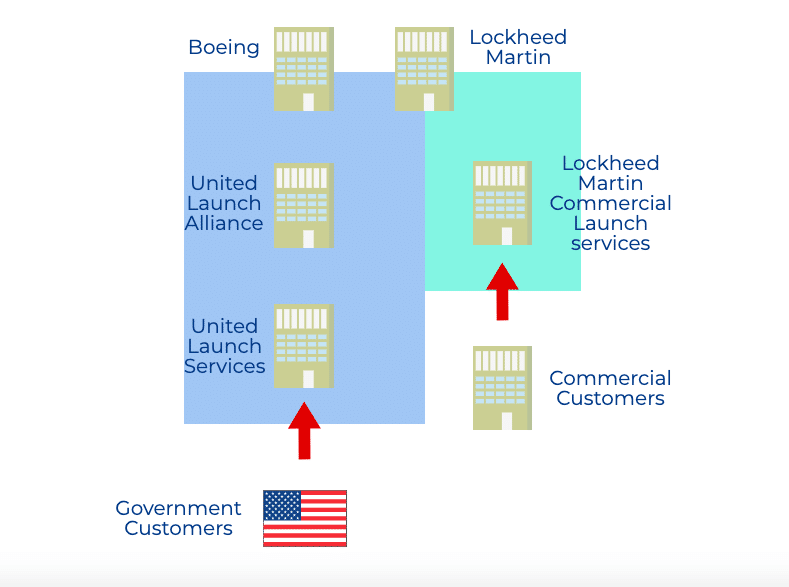
ULA is a joint venture between Lockheed Martin and Boeing, and the launch service agreement for AtlasⅤ is a bit complicated.
The agreement will be with United Launch Services, a subsidiary of ULA for government launches, and Lockheed Martin Commercial Launch Services (LMCLS) for commercial launches (Lockheed Martin has both ULA and LMCLS). Parent company).
Reference: AtlasV Launch Services User ’s Guide March 2010
AtlasⅤ will be used for commercial launches as well as military purposes.
In March 2014, Lockheed Martin announced a service to reflight or compensate for the cost of a failed AtlasⅤ launch (excluding government customers).
Although the price does not decrease, it is said that there will be no need to provide insurance for launch (still necessary for the hardware side of the satellite), so it can be said that it is a service that can only be done because of the reliability of AtlasⅤ.
Activity in planetary exploration
AtlasⅤ has traditionally made significant contributions to planetary exploration missions. Below are typical missions in chronological order.
Extrasolar exploration
It was used to launch the New Horizons space exploration satellite in January 2006.
New Horizons swung-by (accelerated using gravity) Jupiter in February 2007 and successfully observed Pluto in 2015.
Then, on January 2, 2019, succeeded in observing Ultima Thule (current name: Arrokoth), the furthest astronomical object directly observable by humans at the outer edge of the solar system.

Ultima Thule (current name: Arrokoth)
Credit: NASA
Lunar exploration
In June 2009, it was used to launch the Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter (LRO) and the Lunar Crater Observation and Sensing Satellite (LCROSS).
ECROSS is a satellite for observing objects generated by colliding with the moon, and LRO photographed the Apollo11 landing point.

Apollo11 landing point
Credit: NASA
Jupiter Exploration
In August 2011, it was used to launch the Jupiter spacecraft Juno.
Juno observes the change in the magnetic field of Jupiter, and recently Jupiter with the shadow of a satellite.
Mars Exploration
It is no exaggeration to say AtlasⅤ is a regular on Mars exploration.
※For the Spirit and Opportunity, another launch vehicle "Delta II" of ULA is used.
First, it was used to launch the Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) in November 2011.
The MSL is loaded a spacecraft, Curiosity, which collects and analyzes Martian soil and rocks.
In November 2018, it was used to launch Insight for observe Mars underground.
And 2020 is the year when the orbit to Mars opens.
On July 17, a new spacecraft Mars 2020 will be launched from Cape Canaveral Air Force Base.
Mars 2020 has named Perseverance by our vote.
Curiosity of mankind drives
In addition to these planetary explorations, a solar observation satellite (Solar Dynamics Observatory: SDO) was launched in February 2010.
※A solar observation satellite jointly developed by NASA and ESA on February 9, 2020. has scheduled launch however it was postponed due to COVIS-19.
In this way, AtlasⅤ has continued to contribute to humanity's quest for the unknown through the launch of a planetary probe.
Manned spacecraft star liner opens up a new era
A test flight of manned spacecraft Starliner, which Boeing is developing, conducted on December 20, 2019, and a manned flight test with an actual astronaut on board will conduct in November 2020.
In the unmanned flight test in December, the orbital injection failed, and there are concerns about the impact on future development such as other discovered troubles and costs, but the beginning of new era is expected.
Comic "New Era in Space"
The comic above is created by @_Pkrin, who belongs to the online salon "Anman Salon" managed by @wakanjyu321, Japanese genius / beautiful manga artist. Grateful thanks!
Click here for "Anman Salon" which can deal with the mission of space law and rocket girls project.
AtlasⅤ has long contributed not only to launching commercial and military satellites, but also to exploration of planets such as Mars.
The success of many missions must have been supported by the inquisitiveness and curiosity of mankind. In the opening comic, she looked cool and actually curious.
Cutie fairing ponytail!
The opening of the route to Mars, 2020, will be the year when a new era will begin, following Mars exploration and manned flight by private companies.
ULA is developing a new launch vehicle, Vulcan.
The roads that AtlasⅤ has carved out are continually curiosity and inquisitiveness.
Reference:
・ AtlasV Launch Services User ’s Guide March2010
https://www.ulalaunch.com/docs/default-source/rockets/atlasvusersguide2010.pdf
・ The Annual Compendium of Commercial Space Transportation: 2018 Federal Aviation Administration
・ A book about the whole space project
この記事が気に入ったらサポートをしてみませんか?
