
Epsilon in 3 minutes
Epsilon is a launch vehicle developed by Japanese rocket maker IHI Aerospace.
It has been launched from the Uchinoura Space Center in Kagoshima Prefecture as a successor to the M-V that was abolished in 2006.

Reference:JAXA website "Epsilon Rocket"
The name "Epsilon" comes from "Evolution & Excellence", "Exploration" and "Education", and also means that it inherits the Japanese solid rocket technology of Λ (lambda) and M (mu).
Epsilon has the features of ①solid rocket, ②small size, and ③innovativeness.
Traditional solid fuel rocket
One of the features of Epsilon is that it is a solid rocket.
This is a launch vehicle that uses a propellant made of solid fuel (such as liquid synthetic rubber) and an oxidizer (such as ammonium perchlorate).
On the other hand, launch vehicle that use liquid fuel (such as liquid hydrogen) and oxidizers (such as liquid oxygen) are called liquid rockets. For example, H-ⅡB main engine and Falcon 9(from Space X) engine.
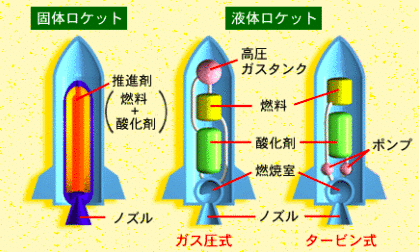
Reference:JAXA website "Space Information Center"
Solid rocket have the advantage of being simple structure and easy to handle, but have the disadvantage of being unable to re-ignite because it will be only launched after ignition(imagine rocket firework), making it difficult to transfer precisely to orbit.
On the other hand, liquid rocket can adjust thrust and enable to transfer precisely to orbit, but have the disadvantage that they are difficult to handle (for example, liquid hydrogen is -253℃ and complicated structure).
Solid rocket have a long history, dating back to the Pencil Rocket that Japanese professor Hideo Itokawa started development in 1954.
Since then, R&D on solid rocket have been continued through Λ and M. Epsilon is a domestic launch vehicle that inherits that tradition.
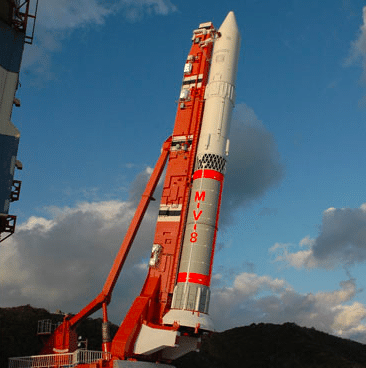
M-Ⅴ(Reference: JAXA website “M-Ⅴ rocket”)
M-Ⅴ transferred Hayabusa which returned to Japan in 2010.
In addition, Epsilon can be used with a liquid fuel engine, and improve the accuracy of orbital transferring.
【M-Ⅴ Issues and abolition】
M-V is a solid rocket developed by the Institute of Space and Astronautical Science (ISAS, currently JAXA Space Science Institute) for research on solid rocket and launching satellites.
The launch required around 8 billion JPY and around 3 years development period. It was abolished in July 2006 to develop more affordable/small launch vehicle and maintain solid rocket technology in Japan.
Small launch vehicle for meet small satellite launch needs
Another feature of Epsilon is its small size.
It is 26m in length, 2.6m in diameter and 96t in weight. Compared to the same Japanese launch vehicle, H-ⅡB, which is 56.6m in length, 5.2m in diameter (first stage) and 531t in weight, it is much smaller.
It can transfer 1500 kg to low orbit (about 200 to 500 km, LEO) and 590 kg to solar synchronous orbit (about 600 to 900 km, SSO).
It plays a role in expanding opportunities for launching small satellites that are small or over-costed to load on H-ⅡB and others.
Introducing innovative systems
The third feature is a system that enables inspection and control with less resources. Epsilon performs its own inspection of the equipment before launch by AI.
In theory, it is possible to access the network from anywhere in the world and control it, and it is said to be the ultimate control system that does not depend on the launch site (JAXA).
It can be said that it is a launch vehicle that "inherits tradition and continues to innovate."
Four times launches
Epsilon has been active in all four launches so far.
Test model
First, on September 14, 2013, the planetary space telescope "Hisaki" was launched by the test model.
Hisaki, the world's first space telescope for observing planets, observes the effects of the solar wind on Jupiter.
Epsilon-2
On December 20, 2016, Epsilon-2 was launched for transferring the geospace exploration satellite "ARASE".
Geospace is the space near Earth.
It is said that there is a radiation zone (Van Allen zone) that contains a lot of high-energy particles. The mission is to elucidate how this happens.
Epsilon-3
On January 18, 2018, the satellite "ASNARO-2" equipped with a high-performance small radar was launched by Epsilon-3.
This satellite is a remote sensing satellite that can observe the earth with high resolution.
Epsilon-4
And on January 18, 2019, Epsilon-4was launched, and at that time the innovative satellite technology demonstration was conducted.
This is like an experiment to demonstrate the theme selected in the open call on orbit (see below).
At this time, multiple CubeSats (small satellites) are also loaded, including the satellites that create artificial shooting stars.
Epsilon is also contributing to the creation of space entertainment.
Position in the Basic Plan on Space Policy-Synergy with H3
According to the timetable for the Basic Plan on Space Policy, Epsilon will be used for "publicly offered small projects" and "innovative satellite technology demonstrations".
【Open call small type】
The spacecraft/scientific satellite project using Epsilon with a total funding of less than 15 billion yen from JAXA.
【Innovative satellite technology demonstration】
This is a program to demonstrate basic parts and technologies using small satellite. It can be have the opportunity to create innovation by developing and verifying challenging and high-risk satellite technologies / missions.
From 2020 onwards, it is said that synergy with H3 will be promoted in order to smoothly transition from H-IIA / B to the H3.
Specifically, the first stage of Epsilon and the solid rocket booster of H3 will be shared, and the technology developed in the second stage of Epsilon will be applied to H3.
This is expected to improve development efficiency and reduce costs.
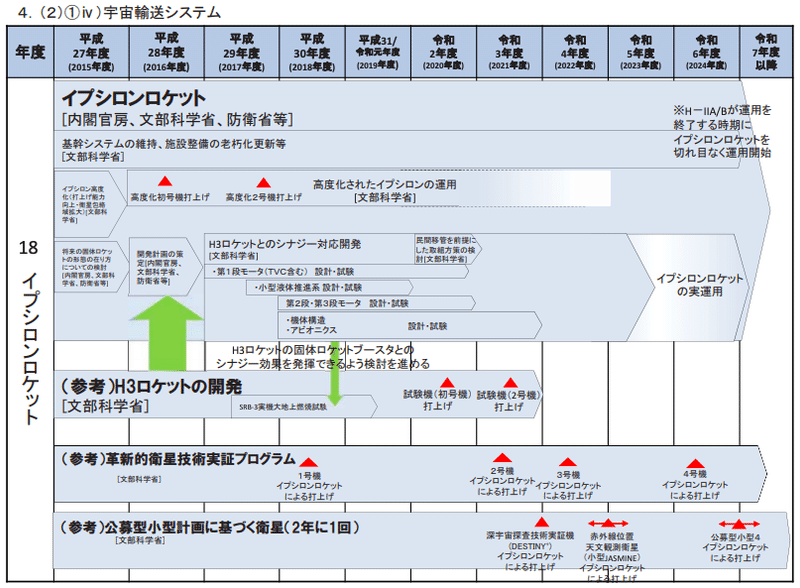
Reference: Basic Plan on Space Policy Schedule (Revised in 2019)
Conclusion
In this way, Epsilon continues to innovate while continuing its tradition, but it is important to see what kind of outcomes will be achieved in recent years as increasing the needs for launching small satellite.
Comic "Evolutionary idol !!"
The comic above is created by @_Pkrin, who belongs to the online salon "Anman Salon" managed by @wakanjyu321, Japanese genius / beautiful manga artist. Grateful thanks!
Click here for "Anman Salon" which can deal with the mission of space law and rocket girls project.
Epsilon features solid rocket, small size, and innovation. This article focuses on these.
If we characterize this as a character, a small but fast-moving solid rocket can be said to be a symbol of energy, and the innovation and entertainment element in the demonstration program can be said to be idleness. In the design, these elements were reproduced beautifully.
In addition, the synergy with H3, which is described in the Basic Plan on Space Policy, cannot be overlooked.
How will the new value created by "sharing" the first stage of Epsilon with the side booster of H3 and, so to speak, standing on the same stage affect the Japanese space industry? Look forward to the day of the actual performance.
Reference:
・ Epsilon Launch Vehicle User's Manual JAXA
・ Status of key rocket initiatives JAXA
https://www8.cao.go.jp/space/comittee/27-kiban/kiban-dai46/pdf/siryou3-1-1.pdf
・Implementation Schedule of the Basic Plan on Space Policy
・Epsilon Rocket JAXA
http://www.jaxa.jp/projects/rockets/epsilon/pdf/rocket07.pdf
・ The 36th Science and Technology Council Research Plan ・ Evaluation Subcommittee Space Development and Utilization Subcommittee Synergy development with Epsilon rocket H3 launch vehicle JAXA
http://www.jaxa.jp/press/2017/07/files/20170704_epsilon_j.pdf
この記事が気に入ったらサポートをしてみませんか?
